www.aljazeerah.info
Opinion Editorials, February 2021
Archives
Mission & Name
Conflict Terminology
Editorials
Gaza Holocaust
Gulf War
Isdood
Islam
News
News Photos
Opinion Editorials
US Foreign Policy (Dr. El-Najjar's Articles)
www.aljazeerah.info
While Corporate Deep-Sea Mining Threatens Mexico's Marine Life, 3 Abundant Plants Could Represent an Energy Revolution By Shannon Collins and Carlisle Johnson Mexico News, February 7, 2020 |
 |
 |
|
The jatropha curcas plant is a source of biodiesel, file, January 22, 2021 |
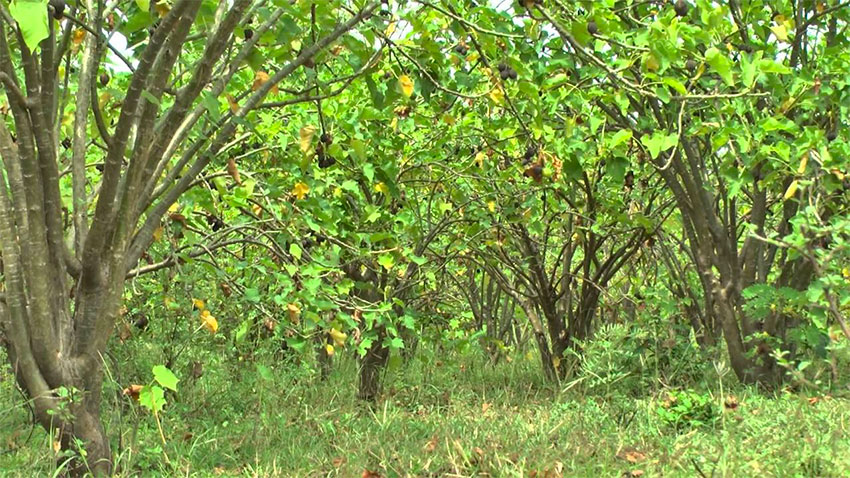
Relicanthus sp, one of many creatures found in a proposed deep-sea mining area in the eastern Clarion-Clipperton Zone, file, February 2, 202 |
Corporate deep-sea mining dreams threaten Mexico’s marine life
By Shannon Collins
Mexico News, February 2, 2021
Contracts to dredge the ocean's floor for resources could destroy aquatic habitats
Until recently, very little was known about the deep sea. Beyond the Midnight Zone — 1,000 and 4,000 meters below the water’s surface, where no sunlight penetrates — it was largely assumed that the seabed was essentially barren, barring a few creatures that generate their own light.
Evolution was thought to rely on the energy of the sun, which cannot penetrate more than 1,000 meters down, meaning that life should not be able to evolve on the seafloor. This was the commonly held view until 1977, when marine biologists near the Galapagos Islands discovered hydrothermal vents teeming with life. In a nod of poetic justice to Charles Darwin himself, this new information sent the marine biology community into a frenzy.
It became apparent that life could evolve in both the Abyssal Zone — between 4,000 and 6,000 meters below the surface — and the Hadal Zone — anything more than 6,000 meters below the surface — in conditions which hitherto it was thought that no life on Earth could survive.
In 1982, the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea established the Law of the Sea Treaty, a document that stated that the world’s oceans should be preserved for the future as part of “the common heritage of mankind.” This same UN convention also took the initial steps in the establishment of the International Seabed Authority (ISA), the regulatory body overseeing the exploration and exploitation of minerals in the international seabed.
But far from safeguarding the oceans from the destructive effects of human activities, the ISA has largely disregarded environmental concerns and shown itself to facilitate access to deep-sea mining companies, entering 30 15-year contracts with countries across the globe that license the exploration of the deep seabed for minerals, 18 of which are in the Clarion-Clipperton zone, off the west coast of Mexico.
The Clarion-Clipperton Zone, in international waters, lies between Hawaii and Mexico.
The main draw for deep-sea mining companies is an abundance of polymetallic nodules found on the deepwater plains, containing copper, manganese, cobalt, and nickel — all crucial in modern batteries — in greater concentrations than have previously been found on land.
At full capacity, mining companies expect to dredge thousands of square miles per year, and even the most conservative guesses at the impact of such an operation suggest that huge swathes of the seabed will be covered in sediment, likely resulting in the destruction of entire habitats.
To date, there are 16 contracts sanctioning the exploration of the Clarion-Clipperton Zone, half of which are split between just four private entities, including the United States arms manufacturer Lockheed-Martin. An extensive — and damning — report by Greenpeace in late 2020 criticized the murky corporate practices surrounding the acquisition of contracts by these parent companies, raising questions of accountability and transparency.
Meanwhile, U.S.-based Odyssey Marine Exploration, through its Mexican subsidiary Exploraciones Oceanicas, is pushing forth with its proposed phosphate seabed mining in the Mexican Exclusive Economic Zone, despite two rejected permits in 2016 and 2018. Located 40 kilometers off the Pacific Coast of Baja California Sur are an estimated 588 million tonnes of phosphate ore, which Odyssey believes is an essential resource to give Mexico sovereignty over the production of its food.
Also located off the coast of Baja California Sur is a diverse marine ecosystem that is crucial to the survival of the thousands of grey whales that migrate there to give birth to their young, as well as to blue whales, humpback whales, and the endangered loggerhead turtle. The large dredging ships that would be used to extract the phosphate would disturb an area roughly equivalent to 60% of Mexico City.
Alex Olivera from the Center for Biological Diversity explains how this “deep-sea mining project is a threat to whales, turtles and other marine species of interest to commercial fishing. The area is of great importance for the loggerhead turtles and is within the migration route of the gray whales.
If it is carried out, there will be environmental impacts due to the dredging of the seafloor by removing all organisms and resuspending the sediments, which likely contain elements that are toxic to the environment.”
But who really stands to gain from such an endeavor? Given the harmful effects of phosphate on the environment, it would seem that governments should be searching for a less harmful solution to increasing food demands — one which does not rely on the potential destruction of the seabed.
At this level, however, the problem is bogged down in the prehistoric belief that all investment is good investment. As such, mining companies are simply unwilling to engage with the future ramifications of deep-sea mining, pursuing material gain as a short-term solution that trumps untold long-term consequences. Governments, largely, are unwilling and unable to hold these multinational behemoths to account, especially where locations are politically, geographically and economically removed from the countries and states which will bear the brunt of the impact.
The leading proponents of deep-sea mining, in particular, present themselves as the only viable alternative to terrestrial mining, which has historically caused a litany of social and political inequities across the globe and has had a hugely harmful environmental impact.
Companies such as DeepGreen, a Canadian deep-sea mining firm, argue that some biodiversity loss is inevitable and should be seen as a small sacrifice to make to mitigate the harmful effects of terrestrial mining, though there is, in fact, little evidence that deep-sea mining is a necessary evil for the transition to sustainable economies, particularly if governments pay heed to the urgent need for efficient distribution of resources and increasingly circular economies.
And yet it is abundantly clear that the problem is not merely philosophical but is in fact a distressing reality that threatens to destroy one of the final relatively untouched ecosystems on the planet. Most of us are already familiar with the laundry list of damages that have already been wreaked upon the ocean, not the least of which are overfishing, pollution and the increasing prevalence of microplastics in food chains and water supplies. Recently there is the shocking discovery that plastic particles can be found in the embryos of unborn children.
The deep ocean represents more than 95% of habitable space on Earth, and yet, for the most part, we know as little about it as we do the furthest reaches of the galaxy. To embark on a mission predicated on its partial destruction for capital gain seems the pinnacle of madness and will likely only exacerbate biodiversity loss and ecosystem destruction already being witnessed on the land.
***
Shannon Collins is an environment correspondent at Ninth Wave Global, an environmental organization and think-tank. She writes from Campeche.
Corporate deep-sea mining dreams threaten Mexico's marine life (mexiconewsdaily.com)
***
These 3 plants could represent an energy revolution for Mexico
By Carlisle Johnson
Mexico News, January 22, 2021
A common weed, castor beans and sugar could replace imports of diesel, lubricating oil and gasoline
It has been frequently noted that the colors on a nation’s flag relate to its struggle for independence: red for blood spilled in the course of revolution is probably the most common example. By that metaphor, Mexico could be the planet’s greenest nation, through an energy revolution.
Mexico has it all, but doesn’t seem to realize it yet. There’s no need to belabor the point that Mexico’s abundant sunshine and winds are green sources. Mexico is blessed by sunlight over its entire territory, and the fierce winds crossing places such as the Isthmus of Tehuantepec are far more than gentle zephyrs.
I’m referring to practically unknown Jatropha curcas, equally obscure Ricinus and better known Saccarum, sugar cane, presumably now in surplus as a result of President López Obrador’s crackdown on sweets.
As a bonus, Jatropha and Ricinus grow wild on the most marginal of land, even roadsides. Diesel, lubricating oil and gasoline are three more better-known names for the three. Mexico imports all three, but needn’t.
Jatropha curcas is a weed, often used as a fence post by poorer, non-corporate farmers in Mexico’s hard hit, more rural areas. You’ve probably driven by it thousands of times without knowing it’s renewable and an excelled feedstock for diesel. Think of it as the girl next door or rather one of a pair of attractive next door twins you’ve overlooked while growing up.
The second attractive twin next door you’ve driven by countless times is wild Ricinus, slightly better known as the castor bean, far better known as the not-so-secret ingredient in world famous Castrol premium motor oil. Both are sustainable and farmable, although “I grow fence posts” is not a glamorous pick-up line at a farm convention. And castor beans are toxic and require careful handling.
So while mega-refiner Phillips is converting a major California refinery to run on used cooking oil from restaurants, Mexico could be sitting pretty.
I’ve left Saccarum, or sugar cane, until last as its story is better known. Sugar cane based ethanol is 10 times as profitable as heavily subsidized corn-based ethanol in the U.S., already as E10 or E15 mandated in the U.S. and widely in Europe; and doesn’t harm engines in vehicles from 1996 on (probably even earlier as my 1988 Toyota can attest).
Maybe the next time you see the red, white and green, think what the green could stand for.
***
Carlisle Johnson writes from his home in Guatemala.
These 3 plants could represent an energy revolution for Mexico (mexiconewsdaily.com)
***
Share the link of this article with your facebook friends
|
|
|
|
||
|
||||||